Energy efficiency in the cloud
Posted by Urs Hoelzle, Senior Vice President for Technical Infrastructure (Cross-posted on the Google Green Blog .) At Google, we’re obsesse...
https://iskablogs.blogspot.com/2012/06/energy-efficiency-in-cloud.html
Posted by Urs Hoelzle, Senior Vice President for Technical Infrastructure
(Cross-posted on the Google Green Blog.)
At Google, we’re obsessed with building energy efficient data centers that enable cloud computing. Besides helping you be more productive, cloud-based services like Google Apps can reduce energy use, lower carbon emissions and save you money in the process. Last year, we crunched the numbers and found that Gmail is up to 80 times more energy-efficient than running traditional in-house email. We’ve sharpened our pencils again to see how Google Apps as a whole—documents, spreadsheets, email and other applications—stacks up against the standard model of locally hosted services. Our results show that a typical organization can achieve energy savings of about 65-85% by migrating to Google Apps.
Lower energy use results in less carbon pollution and more energy saved for organizations. That’s what happened at the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), which recently switched approximately 17,000 employees to Google Apps for Government. We found that the GSA was able to reduce server energy consumption by nearly 90% and carbon emissions by 85%. That means the GSA will save an estimated $285,000 annually on energy costs alone, a 93% cost reduction.
How is the cloud so energy efficient? It’s all about reducing energy use for servers and server cooling. Here’s how it works:
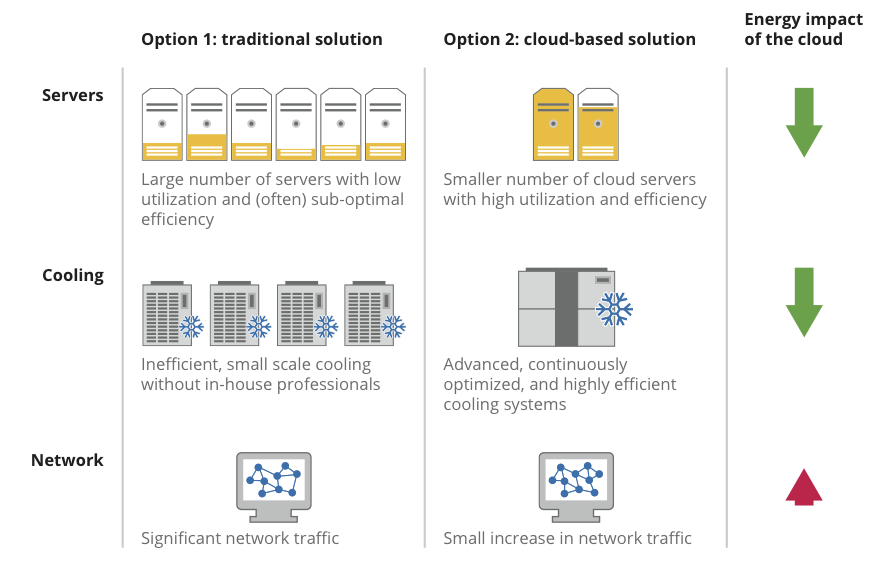
A typical organization has a lot more servers than it needs—for backup, failures and spikes in demand for computing. Cloud-based service providers like Google aggregate demand across thousands of people, substantially increasing how much servers are utilized. And our data centers use equipment and software specially designed to minimize energy use. The cloud can do the same work much more efficiently than locally hosted servers.
In fact, according to a study by the Carbon Disclosure Project, by migrating to the cloud, companies with over $1 billion in revenues in the U.S. and Europe could achieve substantial reductions in energy costs and carbon emissions by 2020:
We’ve built efficient data centers all over the world, even designing them in ways that make the best use of the natural environment, and we continue working to improve their performance. We think using the super-efficient cloud to deliver services like Google Apps can be part of the solution towards a more energy efficient future.
(Cross-posted on the Google Green Blog.)
At Google, we’re obsessed with building energy efficient data centers that enable cloud computing. Besides helping you be more productive, cloud-based services like Google Apps can reduce energy use, lower carbon emissions and save you money in the process. Last year, we crunched the numbers and found that Gmail is up to 80 times more energy-efficient than running traditional in-house email. We’ve sharpened our pencils again to see how Google Apps as a whole—documents, spreadsheets, email and other applications—stacks up against the standard model of locally hosted services. Our results show that a typical organization can achieve energy savings of about 65-85% by migrating to Google Apps.
Lower energy use results in less carbon pollution and more energy saved for organizations. That’s what happened at the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), which recently switched approximately 17,000 employees to Google Apps for Government. We found that the GSA was able to reduce server energy consumption by nearly 90% and carbon emissions by 85%. That means the GSA will save an estimated $285,000 annually on energy costs alone, a 93% cost reduction.
How is the cloud so energy efficient? It’s all about reducing energy use for servers and server cooling. Here’s how it works:
A typical organization has a lot more servers than it needs—for backup, failures and spikes in demand for computing. Cloud-based service providers like Google aggregate demand across thousands of people, substantially increasing how much servers are utilized. And our data centers use equipment and software specially designed to minimize energy use. The cloud can do the same work much more efficiently than locally hosted servers.
In fact, according to a study by the Carbon Disclosure Project, by migrating to the cloud, companies with over $1 billion in revenues in the U.S. and Europe could achieve substantial reductions in energy costs and carbon emissions by 2020:
- US companies could save $12.3 billion and up to 85.7 million metric tonnes of CO2
- UK companies would save £1.2 billion and more than 9.2 million metric tonnes of CO2
- French companies could save nearly €700 million and 1.2 million metric tonnes of CO2
We’ve built efficient data centers all over the world, even designing them in ways that make the best use of the natural environment, and we continue working to improve their performance. We think using the super-efficient cloud to deliver services like Google Apps can be part of the solution towards a more energy efficient future.




